The Different Types of Business Structures | EduPristine

What are Different Types of Business Structures?
In the ever-evolving world of business, the key to sustained success goes beyond just the products or services a company offers. At the core of every thriving business is its organizational framework – the business structure. This essential element not only shapes how a company operates internally but also influences its interactions with the outside world.
In this blog we will make an effort to understand the complexities of business structures, exploring a variety of setups, each carrying its own implications and advantages. From one-person ventures in sole proprietorships to the intricate hierarchies of large corporations, the choices businesses make in how they structure themselves hold significant consequences. So, let’s get started!
But before that we feel it’s important to first clear what is a business structure.
What is a business structure?
A business structure refers to the legal and organizational framework adopted by a company. It outlines how the business is organized, operated, and owned. This structural decision holds significant implications for various aspects of the business, such as taxation, liability, and management.
Business structures come in various forms, including sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and limited liability companies (LLCs). The choice of structure depends on factors like the size of the business, the number of owners, and the desired level of personal liability protection. Understanding these structures is pivotal for entrepreneurs and business enthusiasts alike, as it sets the groundwork for the overall success and sustainability of a business.
Now, with a fair understanding of the basics, we will move forward and understand the different structures of the business.

What are the different structures of business?
The different forms of business are as follows:
1. Sole Proprietorship:
A sole proprietorship is the simplest and commonly found form of business structure. In this setup, a single individual owns and operates the entire business. The owner is fully responsible for all aspects of the business, including its profits, losses, debts, and day-to-day operations.
Key Characteristics:
- Ownership: The business is entirely owned by one individual, known as the sole proprietor. This individual makes all the decisions and retains all the profits.
- Liability: The owner has unlimited personal liability. This means that personal assets could be used to settle business debts if the business encounters financial difficulties.
- Decision-Making: The sole proprietor has complete control and autonomy over decision-making. This streamlined decision process allows for quick responses to market changes.
- Taxation: Business income is typically reported on the owner’s personal tax return. This structure simplifies tax filing, as there is no separate business tax return.
- Flexibility: Sole proprietorships are easy to start and dissolve. There are minimal formalities and paperwork involved in establishing this type of business.
Advantages:
- Simplicity and ease of setup.
- Direct control over business operations.
- Minimal bureaucratic requirements.
Challenges:
- Unlimited personal liability.
- Limited capacity for business expansion.
- Dependency on the owner’s skills and resources.
Sole proprietorships are often favored by small businesses, freelancers, and consultants due to their simplicity and low administrative burden. However, individuals opting for this structure should carefully consider the potential personal liability implications and assess the scalability of their business.
2. Partnership
A partnership is a business structure where two or more individuals join forces to manage and operate a business in accordance with the terms set out in a Partnership Deed. This legal document frames the rights, responsibilities, and profit-sharing arrangements among the partners. Partnerships are a popular choice for businesses that benefit from the complementary skills and resources of multiple individuals.
Key Characteristics:
- Ownership:Partnerships involve two or more individuals, known as partners, who share ownership of the business. Each partner contributes capital, skills, or assets to the venture.
- Liability: In a general partnership, each and every partner has unlimited personal liability for the debts and obligations of the business. Limited partnerships exist where some partners have limited liability, but they typically don’t play an active role in the management.
- Decision-Making:Partnerships often benefit from shared decision-making, with each partner contributing to the strategic direction and day-to-day operations of the business.
- Profit-Sharing:Profits and losses are typically shared among the partners based on the terms present in the Partnership Deed. This agreement also addresses issues like the distribution of responsibilities and dispute resolution.
- Taxation:Like sole proprietorships, partnerships experience pass-through taxation, where business profits and losses pass through to the individual partners, who then report them on their personal tax returns.
Advantages:
- Diverse skills and resources from multiple partners.
- Shared decision-making and responsibilities.
- Flexibility in profit distribution.
Challenges:
- Unlimited personal liability for general partners.
- Potential for conflicts between partners.
- Limited ability for the business to raise capital compared to a corporation.
Partnerships are a flexible and collaborative structure, suitable for various industries. Clear communication and a well-drafted Partnership Deed are essential to navigating potential challenges and ensuring the success of the business venture.
3. Corporation
A corporation is an independent legal entity distinct from its owners, who are identified as shareholders. It is formed under state law and is characterized by a complex structure that includes shareholders, a board of directors, and officers. Corporations are considered separate legal entities, providing limited liability protection for their shareholders.
Key Characteristics:
- Ownership: Shareholders are the owners of a corporation. They invest in the company by purchasing shares of stock, which represent ownership and may entitle them to voting rights and dividends.
- Liability: Limited liability stands out as a key benefit of the corporate structure. Shareholders are typically not personally responsible for the debts and liabilities of the corporation, protecting their personal assets.
- Management: Corporations have a hierarchical management structure. Shareholders elect a board of directors, who, in turn, appoint officers (such as CEO, CFO, etc.) to oversee the day-to-day operations.
- Decision-Making: Major decisions are made by the board of directors, representing the interests of the shareholders. Shareholders often vote on significant matters, such as mergers or changes to the corporate charter.
- Taxation: Corporate entities are liable to pay corporate income tax.
Profits are taxed at the corporate level, and if dividends are distributed to shareholders, they may also be subject to individual income tax.
Advantages:
- Limited liability for shareholders.
- Enhanced ability to raise capital through the sale of stocks.
- Perpetual existence, regardless of changes in ownership.
Challenges:
- Complex regulatory requirements and formalities.
- Taxation of profits at both the corporate and individual levels, resulting in double taxation.
- More extensive administrative and reporting obligations.
Corporations are often chosen by larger businesses aiming for significant growth and seeking access to public financial markets. The structured governance and limited liability protection make corporations an attractive option, but potential drawbacks include increased administrative burdens and tax complexities.
4. Limited Liability Company (LLC)
A Limited Liability Company (LLC) is a popular business structure that combines elements of both partnerships and corporations. LLCs offer the advantage of limited liability protection for their members while providing flexibility in management and taxation.
Key Characteristics:
- Ownership: Members, not shareholders, own an LLC. Members can encompass individuals, corporations, or other LLCs. The ownership structure is flexible, and members’ roles and responsibilities are outlined in the operating agreement.
- Liability: The primary benefit of an LLC is limited liability. Typically, members bear no personal responsibility for the company’s debts and liabilities. This protection shields their personal assets from business-related obligations.
- Management: LLCs can be managed by their members or by appointed managers. This flexibility allows members to actively participate in the day-to-day operations or delegate management responsibilities to non-members.
- Decision-Making: Decision-making authority in an LLC is often outlined in the operating agreement. Members can choose to make decisions collectively, or they can appoint managers to handle operational choices.
- Taxation: LLCs are subject to pass-through taxation Profits and losses pass through to the members, who then report them on their individual tax returns. Alternatively, an LLC can elect to be taxed as a corporation, providing additional flexibility.
Advantages:
- Limited liability protection for members.
- Flexibility in management and ownership structure.
- Pass-through taxation or the option to be taxed as a corporation.
Challenges:
- Varying regulations and rules by state.
- Complexity in drafting and maintaining an operating agreement.
- Limited ability to raise capital compared to a corporation.
LLCs have gained popularity due to their flexibility, combining the liability protection of a corporation with the simplified management structure of a partnership. The choice of an LLC as a business structure is often favored by small to medium-sized businesses seeking a balance between protection, flexibility, and ease of administration.

Conclusion
As we conclude the blog, it’s evident that the choice of business structure is not a mere formality but a strategic decision that influences everything from decision-making processes to taxation. The journey through sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and LLCs has shed light on the significance of aligning the chosen structure with the unique needs and goals of a business.
In the finance and accounting domain, mastering the details of business structures is an integral part of the ACCA (Association of Chartered Certified Accountants) course. If you’re curious about ACCA course details or wondering, “What is ACCA course all about?” – you’re in the right place. At EduPristine, we take pride in being a Gold Partner of ACCA, a recognition of our commitment to providing quality education. As an accredited Computer Based Exam (CBE) Centre for the ACCA course, we ensure a seamless and efficient examination experience.
Moreover, our dedication to delivering excellence extends to the study material. EduPristine offers ACCA students access to Kaplan content—an esteemed name officially approved by ACCA. This collaboration reflects our commitment to providing students with the best resources to excel -their ACCA journey.
We invite you to connect with EduPristine for a holistic learning experience. To know more about the ACCA course offerings, call our career counsellors today!
MAKE YOUR CAREER IN
Need more Info?
Tags
- ABOUT CFA COURSE
- ABOUT FRM COURSE IN INDIA
- ABOUT THE US CPA COURSE
- ACCA
- ACCA CERTIFICATION
- ACCA COURSE
- ACCA COURSE DETAILS
- ACCA COURSE DURATION
- ACCA COURSE ELIGIBILITY
- ACCA COURSE ELIGIBILITY CRITERIA
- ACCA COURSE ELIGIBILITY IN INDIA
- ACCA COURSE FEES
- ACCA COURSE FEES IN INDIA
- ACCA COURSE IN INDIA
- ACCA COURSE STRUCTURE
- ACCA COURSE STRUCTURE AND FEES IN INDIA
- ACCA COURSE SUBJECTS
- ACCA COURSE SYLLABUS
- ACCA EXAM STRUCTURE AND PATTERN
- ADMISSION TO CFA
- AI-POWERED FRAUD DETECTION IN ACCOUNTING
- APPLICATIONS OF AI IN ACCOUNTING
- AUDITING AND COMPLIANCE
- AUTOMATED DATA ENTRY
- AUTOMATED DATA ENTRY AND PROCESSING
- BAT COURSE
- BEST FINANCIAL MODELING COURSE
- BEST FINANCIAL MODELING COURSE IN INDIA
- BEST ONLINE CFA PREP COURSE
- BEST ONLINE FINANCIAL MODELING COURSE
- CAREER OPPORTUNITIES FOR CPA
- CERTIFICATION
- CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER (CFP®) COURSE
- CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER®
- CERTIFIED FINANCIAL PLANNER® PROGRAM
- CFA
- CFA CERTIFICATION
- CFA COURSE
- CFA COURSE CURRICULUM
- CFA COURSE DETAILS
- CFA COURSE DURATION
- CFA COURSE FEES
- CFA COURSE FEES IN INDIA
- CFA COURSE FULL DETAILS
- CFA COURSE IN INDIA
- CFA COURSE IN INDIA CFA COURSE CFA COURSE DETAILS CFA COURSE SUBJECTS
- CFA COURSE SUBJECTS
- CFA COURSE SYLLABUS
- CFA COURSE TRAINING
- CFA CURRICULUM
- CFA FOUNDATION COURSE
- CFP CERTIFICATION
- CFP COURSE
- CFP COURSE DETAILS
- CFP COURSE FEE
- CFP COURSE FEES IN INDIA
- CFP EXAM
- CFP® COURSE FEES
- CFP® COURSE SYLLABUS
- CFP® ELIGIBILITY
- CMA COURSE
- CMA COURSE DETAILS
- CMA COURSE DETAILS IN INDIA
- CMA COURSE DURATION.
- CMA COURSE ELIGIBILITY
- CMA COURSE ELIGIBILTY
- CMA COURSE FEES
- CMA COURSE FULL DETAILS
- CMA COURSE IN BANGALORE
- CMA COURSE IN INDIA
- CMA COURSE SUBJECTS
- CMA COURSE SYLLABUS
- CMA ONLINE COURSE
- CPA ACCOUNTANT
- CPA COURSE
- CPA COURSE DETAILS
- CPA COURSE DURATION
- CPA COURSE ELIGIBILITY
- CPA COURSE FEES
- CPA COURSE FEES IN INDIA
- CPA COURSE IN INDIA
- CPA COURSE STRUCTURE
- CPA COURSE SYLLABUS
- CPA EXAM
- EVOLUTION OF AI IN ACCOUNTING
- EVOLUTION OF AI IN FINANCE
- FINANCIAL MODELING
- FINANCIAL MODELING AND VALUATION
- FINANCIAL MODELING AND VALUATION COURSE
- FINANCIAL MODELING COURSE
- FINANCIAL MODELING COURSE CURRICULUM
- FINANCIAL MODELING COURSE DETAILS
- FINANCIAL MODELING COURSE FEE
- FINANCIAL MODELING COURSE IN INDIA
- FINANCIAL MODELING COURSE USEFUL
- FINANCIAL MODELING COURSE WITH PLACEMENT
- FINANCIAL MODELLING COURSE
- FINANCIAL MODELLING COURSE DURATION
- FINANCIAL MODELLING COURSE FEES
- FINANCIAL MODELLING COURSE ONLINE
- FINANCIAL RISK MANAGER
- FM COURSE & FRM® COURSE
- FRM
- FRM COURSE
- FRM COURSE CERTIFICATION
- FRM COURSE CURRICULUM
- FRM COURSE DETAILS
- FRM COURSE DURATION
- FRM COURSE ELIGIBILITY
- FRM COURSE FEES
- FRM COURSE IN INDIA
- FRM COURSE SYLLABUS
- FRM® COURSE SUBJECTS
- FRM® COURSE SYLLABUS & HOW TO APPLY FOR FRM® COURSE
- IN FINANCE
- PG PROGRAM IN BUSINESS ACCOUNTING & TAXATION
- PGP BAT COURSE FEES
- PGP BAT COURSE SALARY IN INDIA
- PGP-BAT COURSE
- PGP-BAT COURSE COURSE IN INDIA
- PGP-BAT COURSE DETAILS
- PGP-BAT COURSE DURATION
- PGP-BAT COURSE ELIGIBILITY
- PGP-BAT COURSE FULL FORM
- PGP-BAT COURSE IN INDIA
- PGP-BAT COURSE INSTITUTE IN INDIA
- PGP-BAT COURSE SYLLABUS
- PLACEMENTS TO CFA
- SOFT SKILLS
- TAX PREPARATION
- TAX PREPARATION AND PLANNING
- US CMA COURSE
- US CMA COURSE DETAILS
- US CMA PREPARATION
- US CPA COURSE
- US CPA COURSE DETAILS
- US CPA COURSE FEES
- US CPA COURSE FULL FORM
- US CPA COURSE TRAINING
- US CPA EXAMS
- US CPA MEANING
- US-CMA
- US-CPA
- WHAT IS ACCA COURSE
- WHAT IS CFP® CERTIFICATION?
- WHAT IS CMA COURSE
- WHAT IS CPA COURSE
- WHAT IS FINANCIAL MODELING ALL ABOUT
- WHAT IS FINANCIAL MODELING COURSE
- WHAT IS FRM® COURSE? FRM® COURSE DETAILS
- WHAT IS FRM® COURSE? FRM® COURSE REVIEW
- WHAT IS THE CPA COURSE
- WHAT IS US CPA COURSE?
- WHAT IS US-CMA COURSE
related blogs

Will CMA Online Classes Help You Pass the CMA Exam
Hello, and welcome back to our new blog. Are you preparing to take on the Certified Management Accountant (CMA) journey Read More
Key Insights for CFP® professionals from the 2024 Financial Planning Conclave.
Hello, and welcome back to our new blog. As the financial world continues to evolve, the need for qualified and Read More
What You’ll Learn in Financial Planning Education
CFP® Course Curriculum: What You’ll Learn in Financial Planning Education | EduPristine Welcome back learners to another blog post focusing Read More
Capital Investment Decision in CFA®
Capital Investment Decision in CFA® | EduPristine Welcome back, learners, to another insightful blog post on Capital Investment Decisions in Read More
Techniques Used by CFP Practitioners to Enhance Client Wealth.
Techniques Used by CFP® Practitioners to Enhance Client Wealth | EduPristine Welcome back, financial planning learners! Today’s blog will shed Read More
How to Become a CPA Without a Degree in Accounting.
Hello, and welcome back to our latest blog. Have you ever wondered if you could become a Certified Public Accountant Read More
How Critical is the Role of CFOs in Mergers and Acquisitions
How Critical is the Role of CFOs in Mergers and Acquisitions? Hello, and welcome back to our new blog. In Read More
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Accounting and Finance | EduPristine
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Accounting and Finance | EduPristine Welcome back, learners, to another blog post on the Read More
Role Of CFP® In Bridging the Financial Literacy Gap in India | EduPristine
Role Of CFP® In Bridging the Financial Literacy Gap in India | EduPristine Welcome back, readers, to another insightful blog Read More
A Day in The Life of a Financial Risk Manager ® (FRM®) | EduPristine
A Day in The Life of a Financial Risk Manager ® (FRM ®) | EduPristine Welcome back, readers, to another Read More
How Much Does an US CMA Professional Earn in India by EduPristine
How Much Does a US CMA Professional Earn in India? Hello, and welcome back to our new blog. Have you Read More
Advancing Your Career with a Certified Financial Planner (CFP®) Course | EduPristine
Advancing Your Career with a Certified Financial Planner (CFP®) Course | EduPristine Welcome back learners to another blog post on Read More
US CMA Certification: Helps You Transition into Management Roles
How the US CMA Certification Can Help You Transition into Management Roles? Hello, and welcome back to our new blog. Read More
How the CPA Course Opens Doors to Global Success by EduPristine
How the CPA Course Opens Doors to Global Success? Welcome to our latest blog! Ever wondered what it takes to Read More
Why is Internal Control Crucial for US CMAs | EduPristine
Why is Internal Control Crucial for US CMAs? Hey there, welcome back to our new blog. Have you ever wondered Read More
How Much Does an ACCA Professional Earn in India by EduPristine
How Much Does an ACCA Professional Earn in India? Hey there, so good to have you back again. Have you Read More
PGP-BAT Course Career Opportunities Guide by EduPristine
PGP-BAT Course Career Opportunities | EduPristine Welcome back, learners, to another blog post on the career options ahead of you Read More
The Power of Soft Skills in Financial Leadership (Part I) EduPristine
CFA, FM, and FRM: The Power of Soft Skills in Financial Leadership (Part I) | EduPristine Welcome back, learners, to Read More
How much is a US CPA professional entitled to earn in India?
How much is a US CPA professional entitled to earn in India? Ever thought how your earning potential would skyrocket Read More
The Essentials of Treasury & Liquidity Risk Management in FRM® Course
The Essentials of Treasury and Liquidity Risk Management in FRM® Course | EduPristine Welcome back, learners, to another insightful blog Read More
CMA Course: Unlocking Diverse Career Paths | EduPristine
CMA Course: Unlocking Diverse Career Paths | EduPristine Welcome back, learners, to another blog post on the career paths after Read More
SBI’s Wealth Management: A Growth Prospects for CFP Certified Experts.
How SBI's Wealth Management Creates Opportunities for CFP® - Certified Experts? Hello, and welcome back to our new blog. Have Read More
Can You Get into the Big 4 with the ACCA Qualification?
Can You Get into the Big 4 with the ACCA Qualification? Hi, great to have you back again. One of Read More
CPA License in India- A Game-Changer for Your Accounting Career
Why Earning a CPA License in India is a Game-Changer for Your Accounting Career Hello, so good to have you Read More
Understanding Payroll and Its Components by EduPristine
Understanding Payroll and Its Components by EduPristine Hello there, and welcome back to our latest blog post. Do you have Read More
Safeguarding Success: Tackling Operational Risk in FRM® Course | EduPristine
Safeguarding Success: Tackling Operational Risk in FRM® Course | EduPristine Welcome back, learners, to another insightful blog post on Operational Read More
US CPA Course: Unlocking Diverse Career Paths | EduPristine
The US CPA Course : Unlocking Diverse Career Paths | EduPristine Welcome back, learners, to another blog post on the Read More
Understanding Market Risk within FRM® Course EduPristine
The Pulse of the Market: Understanding Market Risk within FRM® Course Welcome back learners! In this blog post we are Read More
Financial Modelling Course Opportunities | EduPristine
Financial Modelling Course Opportunities by EduPristine Welcome back, learners! In this blog post, we'll explore how completing the financial modelling Read More
Is the ACCA Course Suitable for Working Professionals in India
Is the ACCA Course Suitable for Working Professionals in India? Hello again, and a very warm welcome to our new Read More
Which Path to Take- US CPA vs. Canada CPA?
Which Path to Take- US CPA vs. Canada CPA? Hello, and welcome back to our new blog. Have you ever Read More
Why Should BCom Graduates and Those with 0-2 Years of Experience Pursue the PGP-BAT Course at Edu Pristine
Why Should B.Com Graduates and Those with 0-2 Years of Experience Pursue the PGP-BAT Course at EduPristine? Hi, and welcome Read More
Why the ACCA Qualification is Gaining Popularity in India by EduPristine
Why the ACCA Qualification is Gaining Popularity in India? Hello and welcome back! Have you noticed the number of professionals Read More
ACA vs ACCA What’s the Difference? A guide by Edupristine
Associate Chartered Accountant (ACA) vs Associate of Chartered Certified Accountants (ACCA) Hey there, so good to have you back again. Read More
Ethical Decision Making in Financial Management | Edupristine
Ethical Decision Making in Financial Management Introduction The swift moving world of finance has the ability to have lasting influences Read More
Understanding the Time Value of Money – TVM
What is (TVM) Time Value of Money? The Time Value of Money (TVM) is a fundamental financial principle which asserts Read More
Guide on How to Study for the US CMA Exams | US CMA Course Full Details
Tips & Tricks to Study for the US CMA Exams? Hello, and welcome back to our new blog! We have Read More
CMA Advantages: Benefits of Classroom Training | CMA COURSE | EDUPRISTINE
Why EduPristine's Classroom Training Gives Students a Leading Advantage for CMA COURSE? It is so good to see you again. Read More
Guide to choose an Institute for US CMA program | EduPristine
How to choose an institute for the US-CMA program? Hello, and how have you been? Welcome back! If you have Read More
Core Differences: US CMA vs. Indian CMA
Indian CMA vs US CMA Hello, and welcome back to our new blog where we will be discussing the Indian Read More
The Critical Importance of Soft Skills for CPAs
The Critical Importance of Soft Skills for Certified Public Accountants Hello, and welcome back to our new blog. Have you Read More
Essential Soft Skills for CMAs | US CMA COURSE
Essential Soft Skills for CMAs | US CMA COURSE Hello, and welcome back to our new blog. Have you ever Read More
Guide to Expected Shortfall (ES) by EduPristine
What is Expected Shortfall (ES)? Expected Shortfall (ES) is a way to measure the risk of an investment portfolio focusing Read More
Guide to Choose an Institute for the ACCA Course
How to Choose an Institute for the ACCA course? Hi, so good to have you back again. If you have Read More
BEST INSTITUTE FOR US CPA COURSE IN INDIA | EDUPRISTINE
Hello, and welcome back to our new blog. If you have already decided to pursue the most prestigious US CPA Read More
Guide to Value at Risk (VaR) by EduPristine
What is Value at Risk (VaR)? Introduction Value at Risk (VaR) is a financial metric used to estimate the potential Read More
How to Choose an Institute for the PGP-BAT Program by EduPristine
How to Choose an Institute for the PGP-BAT Program? Hello, and welcome back. It feels great to see you again. Read More
US CPA Eligibility Criteria in India by EduPristine
What is the US CPA Eligibility Criteria in India? Hello, and welcome to our new blog. The ideal accounting candidates Read More
The Cost Involved in Pursuing the ACCA Qualification
What is the Cost Involved in Pursuing the ACCA Qualification? Hello! Welcome back to our new blog. Let me start Read More
Why EduPristine’s Classroom Training Gives PGP-BAT Students a Leading Advantage
Why EduPristine’s Classroom Training Gives PGP-BAT Students a Leading Advantage? Hello, and thank you for being back again. Haven’t we Read More
Why is the FM course gaining popularity in India | EduPristine
Why is the FM course gaining popularity in India? Introduction Hello dear readers, a very warm welcome to all of Read More
Why EduPristine’s Classroom Training Gives ACCA Students a Leading Advantage?
Why EduPristine’s Classroom Training Gives ACCA Students a Leading Advantage? Hello, and welcome to our new blog! If you have Read More
Why is the CFA® course gaining popularity in India | EduPristine
Why is the CFA® course gaining popularity in India? Introduction Hello and welcome back to this brand-new blog where we Read More
Public Accounting vs. Corporate Accounting by EduPristine
Public Accounting vs. Corporate Accounting: A Comprehensive Comparison Hey there, so good to have you back again. Are you at Read More
EduPristine: Empowering Tomorrow’s Finance and Accounting Leaders
EduPristine: Empowering Tomorrow's Finance and Accounting Leaders In a world where there is often a gap between what is taught Read More
Understanding Top Finance Skills Employers Value in 2024 | EduPristine
Understanding Top Finance Skills Employers Value in 2024 In the rapidly evolving landscape of finance, the skills demanded by employers Read More
The Essential Role of Financial Management and Its Purpose | EduPristine
The Essential Role of Financial Management and Its Purpose Hey there, so good to have you back again. Have you Read More
What is Financial Reporting and Why is it Important | EduPristine
What is Financial Reporting and Why is it Important? Hey there, so good to have you back again. Have you Read More
Mastering the Foundations of Accounting by EduPristine
Mastering the Foundations of Accounting Hey there, so good to have you back again! Have you ever wondered what lies Read More
All about Credit Risk: A Comprehensive Guide by EduPristine
All about Credit Risk: A Comprehensive Guide In the domain of finance, managing credit risk is pivotal for the stability Read More
The Critical Role of Performance Management | EduPristine
The Critical Role of Performance Management Hey there, so good to have you back again! Have you ever wondered why Read More
A Comprehensive Comparison of Power BI and Excel | EduPristine
A Comprehensive Comparison of Power BI and Excel Hey there, welcome back again! In today's data-driven world, the ability to Read More
CMA vs MBA: Choosing the Right Path for Your Career Growth
CMA Programa vs. MBA: Choosing the Right Path for Your Career Growth Hey there, so good to have you back Read More
Corporate Governance: A Comprehensive Guide by EduPristine
Corporate Governance: A Comprehensive Guide Welcome to our exploration of Corporate Governance! In this blog, we will delve into the Read More
A Guide to Mastering Payroll Management by EduPristine
Mastering Payroll Management: A Comprehensive Guide to Components, Compliance, and Accounting Entries Hey there, welcome back to our new blog. Read More
Data Analytics for Management Accountants – EduPristine
Data Analytics for Management Accountants Why Data Analytics Matter for Management Accountants Hey there, so good to have you back Read More
Investment Valuation: A Comprehensive Guide by EduPristine
Investment Valuation: A Comprehensive Guide Welcome to our comprehensive guide on investment valuation! In this blog, we'll break down the Read More
Mastering MS Excel: Empowering Accountants for Success | EduPristine
Mastering MS Excel: Empowering Accountants for Success. Hey there, welcome back to our new blog. In the intricate world of Read More
Different Payment Methods for Merger & Acquisition | EduPristine
Different Payment Methods for Merger & Acquisition In the ever-evolving landscape of business, Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) stand as pivotal Read More
Internal vs External Financial Reporting by EduPristine
Internal vs External Financial Reporting Financial reporting is a critical aspect of any organization's communication strategy, serving as a bridge Read More
Difference Between Equity Funds and Mutual Funds by EduPristine
Understanding the Difference Between Equity and Mutual Funds Equity investment and mutual fund investment are both popular choices for long-term Read More
Navigating the ACCA Career Landscape with EduPristine
Navigating the ACCA Career Landscape: Opportunities in India and Beyond Hey there, so good to have you back again! In Read More
Chief Financial Officer (CFO): A Complete Guide | EduPristine
Chief Financial Officer (CFO): A Complete Guide In the dynamic domain of corporate governance, one figure stands out as the Read More
All About Merger and Acquisition by EduPristine
Merger and Acquisition (M&A)? Its What, Why, and When What is M&A? When people hear that a company has taken Read More
What is Income Tax? Part Two by EduPristine
What is Income Tax? Part Two Income tax stands as a pillar of India's economic framework, shaping financial dynamics and Read More
Understanding the Basics of Direct Taxation with EduPristine
Understanding the Basics of Direct Taxation Hey there, so good to have you back again! In the realm of accounting, Read More
The Crucial Role of Ethics in Management Accounting | EduPristine
The Crucial Role of Ethics in Management Accounting Hey there so good to have you back again! Have you ever Read More
What is Income Tax? Part one by EduPristine
What is Income Tax? Part One Income tax serves as a cornerstone in India's financial landscape, wielding significant influence over Read More
Financial Reporting vs. Financial Accounting by EduPristine
Financial Reporting vs. Financial Accounting: Understanding the Basics In the world of business and finance, two key terms often come Read More
How Do Firms Manage Financial Risk | EduPristine
How Do Firms Manage Financial Risk? Managing financial risk is a crucial responsibility for firms in today's dynamic business landscape. Read More
Financial Accounting and Types of Financial Statements | EduPristine
What is Financial Accounting? Exploring Types of Financial Statements Welcome to our exploration of Financial Accounting, a fundamental pillar of Read More
Managerial Accounting- Its Meaning, Process and Types | EduPristine
What is Managerial Accounting? Its Meaning, Process and Types Hello and welcome to the world of managerial accounting—a practical and Read More
A Guide on Project Finance by EduPristine
A Guide on Project Finance In the dynamic landscape of finance, where innovation and strategic thinking converge, one area that Read More
Why do Finance Professionals use Power BI | EduPristine
Why do Finance Professionals use Power BI? Hey there, so good to have you back again! Have you ever found Read More
Macroeconomics: Meaning, Process, and Indicators | EduPristine
Macroeconomics: Meaning, Process, and Indicators Welcome back, students! Today, we're delving into the world of macroeconomics. In this blog, we'll Read More
Internal Audit- Meaning, Objectives, Types and Importance by EduPristine
Internal Audit- Meaning, Objectives, Types and Importance In the world of business, where things can get pretty complex, there's a Read More
A Simple Guide on Quantitative Analysis- EduPristine
What is Quantitative Analysis? A Simple Guide In the ever-changing world of finance, where data holds immense power and decisions Read More
Five Basic Principles of Accounting by EduPristine
What are the Five Basic Principles of Accounting? In the world of finance and business, accounting stands as the backbone, Read More
Internal Controls: Meaning, Types, and Importance by EduPristine
Internal Controls: Meaning, Types, and Importance In the domain of business management, Internal Controls stand as the silent guardians ensuring Read More
Basics of Accounting – Meaning and Basics Concepts | EduPristine
Basics of Accounting - Meaning and Basics Concepts Welcome to the world of Accounting 101 - where numbers tell a Read More
The Different Business Functions by EduPristine
What are the Different Business Functions? In the dynamic landscape of commerce, businesses are intricate entities composed of various interconnected Read More
The Different Types of Business Structures | EduPristine
What are Different Types of Business Structures? In the ever-evolving world of business, the key to sustained success goes beyond Read More
The Vital Role of Cost Management for US-CMAs | EduPristine
The Vital Role of Cost Management for US-CMAs Hey there, so good to have you back again. Have you ever Read More
Role of Ethics and Professionalism in the Investment Industry
Role of Ethics and Professionalism in the Investment Industry In the dynamic landscape of the investment industry, where fortunes are Read More
The Risk Management Process: Essential Steps | EduPristine
The Risk Management Process: Essential Steps In the dynamic landscape of business and finance, uncertainties are inevitable. Every decision, venture, Read More
ACCA vs CPA: Choosing the Right Path for Your Career | EduPristine
ACCA Certification vs. CPA Course: Choosing the Right Path for Your Career Embarking on a career in accounting opens a Read More
Transforming Aspirations into Achievements: CPA Course Excellence
CPA Course Excellence: How EduPristine's Approach Transforms Aspirations into Achievements Embarking on the journey to become a US Certified Public Read More
Comprehensive Guide to ACCA Certification with EduPristine
Unlocking Global Opportunities: A Comprehensive Guide to ACCA Training in India with EduPristine Welcome to your roadmap for global success Read More
CPA Course Decoded: Achieve Success with EduPristine Training
CPA Course Decoded: Achieve Success with EduPristine's Expert-Led Training Embarking on the journey to become a US Certified Public Accountant Read More
US CMA Course: A Step-by-Step Preparation Guide by EduPristine
Master the US CMA Course: A Step-by-Step Preparation Guide by EduPristine Hey there future US CMAs! If you're thinking about Read More
Key Reasons Why Upskilling is Important
As we navigate the challenging yet exciting journey of studying finance and accounting, we wanted to share some valuable advice Read More
All About Evolving Aviation Industry
India’s aviation industry has witnessed significant transformations in recent years, with the emergence of low-cost carriers, the expansion of domestic Read More
How India’s Digital Payment Revolution is Reshaping the Economy
Hey there! So good to have you back again. In this blog, we will discuss the recent developments, explore the significance, Read More
Understand the catastrophic impact of a possible US Debt Default
Hello there! Welcome to our new blog. In this blog post, we will explore the potential catastrophic effects of a Read More
RBI Bids Farewell to Rs. 2000 Notes
Hello there! Welcome to our new blog. In this blog, we will explore the recent decision by the Reserve Bank Read More
Key Insights from the Economic Survey 2022-2023
Hello there, students! How have you been? Today, we will explore more about the recent economic survey, 2022-2023. Economics Read More
What is Digital Marketing? What is the objective?
Hey there! Ever wondered what is the main objective behind practicing digital marketing techniques? Digital marketing has now become a Read More
Why you must consider being a Certified Management Accountant
Hey there! So good to have you back again. Are you someone who loves planning, analyzing, and adjusting monthly Read More
Key Insights from the Economic Survey 2022-2023
Hello there, students! How have you been? Today, we will explore more about the recent economic survey, 2022-2023. Economics plays Read More
What is Digital Marketing? What is the objective?
Hey there! Ever wondered what is the main objective behind practicing digital marketing techniques? Digital marketing has now become a Read More
Why you must consider being a Certified Management Accountant
Hey there! So good to have you back again. Are you someone who loves planning, analyzing, and adjusting monthly budgets? Read More
All About Classroom Training vs Online Training
Hello there, students! How have you been? Today, we will explore more about the recent economic survey, 2022-2023. Economics plays Read More
All About Axis-Citi Acquisition
A significant move initiated by Axis Bank, India’s third largest private sector lender, to acquire Citibank’s retail business has become Read More
Can vernacular edtech ever become mainstream?
Hey there! Glad to have you back again. Did you know that with the next half billion students coming from Read More
Indian start-ups need to start taking corporate governance seriously, why?
Hey there! Glad to have you back again. Wondering why Indian start-ups require corporate governance? If yes, then this blog Read More
How to Level up the Overall Digital Marketing Strategy?
Hello there! So good to have you back. Did you know that more than half of the brands today either Read More
Snapchat for Business
Hey there! Welcome back again. In this blog, we will understand how to use Snapchat for businesses to stand out Read More
What will Digital Marketing Look like in the Next 20 years?
Hey there! Do you wonder what digital marketing will look like in the next 20 years? If yes, then this Read More
Importance of Soft Skills
Hey there! So good to have you back again. In this blog, we will understand the top 5 skills and Read More
Why are Mr. Men and Little Miss characters all over the social media?
Hey there! Welcome back again. If you’re on social media, you must have probably come across Mr. Men and Little Read More
How global firms are looking at the Indian investment market
Hey there! So good to have you back again. Wondering, how the global firms are looking at the Indian investment Read More
Role of Keywords in Digital Marketing
Hey there! Welcome back again. Did you know that a proper keyword search lies at the heart of a successful Read More
All About the Social Media Careers and the Skills to be Mastered
Hey there! Happy to have you back again. Did you know that social media careers are taking off? Well, social Read More
All About Leadership in a Multicultural World
Hey there! Welcome back again. Ever wondered what a global mindset is? If yes, then this blog is a must-read Read More
All about Metaverse and why is metaverse important for brands?
Hey there! Welcome back again. Wondering what exactly Metaverse is? Is it a video game? Or is it just another Read More
Why will the Netflix business model need more than just a quick fix?
Hey there! So good to have you back again! Wondering why the Netflix model will take more than just a Read More
Financial Models and How to Create them Effectively
Hey there! So good to have you back again. In this blog, we will understand how Finance Professionals can create Read More
Top 5 Digital Marketing Trends to be Followed
Hey there! So good to have you back again. Wondering what marketers have been doing so far in 2022? If Read More
Best Practices for Financial Management
Hey there! So good to have you back again. In this blog, we will discuss a few essential tips for Read More
How did the crisis in Sri Lanka impact India?
Hey there! Welcome back again. In this blog, we will discuss how the crisis in Sri Lanka is impacting India. Read More
Objectives of Risk Management
Hey there! So good to have you back again. In this blog, we will answer the most frequently asked question, Read More
Career Options After Qualifying for the US CMA Course
Hey there! So good to have you back again. Are you curious and want to learn more about the job Read More
Skills That Make You Proficient in Digital Marketing
Did you know that digital marketing is a dream job for many people today? Let us find out why? If you are Read More
What Are The Different Types of Financial Markets?
Hey there! Welcome back once again. In the last few blogs, we discussed the financial markets and their functions. We Read More
How Indian Students Can Pursue the US CPA?
Hey there! So good to have you back again! Are you also wondering how can Indian students acquire the international Read More
Equity Derivatives and Benefits of Equity Derivatives
Hey there! Welcome back again. Ever wondered what are Equity Derivatives? If yes, then this blog is a must-read. Equity Read More
What are Black Swans in Risk Management?
Hey there! So good to have you back again. Are you wondering what the term “Black Swans” in risk management Read More
Will Digital Marketing Replace Traditional Marketing?
Hey there! Welcome back again. One of the most frequently asked questions we often get is, will digital marketing ever Read More
Functions of Financial Markets?
Hey there! Welcome back to another blog on finance. In the previous blog, we discussed what are financial markets and Read More
How to Calculate GST (Goods and Services Tax)?
Hey there! So good to have you back again. Are you also keen on learning how to calculate GST? If Read More
Why are Financial Markets Regulated?
Hey there! Welcome back again. Are you also curious and wondering why are financial markets regulated and why are they Read More
Does an Accountant Need an MBA?
Hey there! Welcome back again. Are you the one among others who is confused and want to know whether an Read More
Why is ACCA Not Recognized in The USA?
Hey there! Welcome back again. Have you ever wondered why is the ACCA course not recognized in the USA, but US CPA Read More
Is the US CMA Course Appropriate for Working Professionals?
Hey there! Are you a working professional and want to pursue the US CMA course simultaneously while working full time? If yes, Read More
What is a Derivative?
Derivatives are financial contracts that derive their value from the performance of an underlying asset, or group of assets, or Read More
What is Derivative Market?
Did you know that derivatives are also considered advanced investing? Well, derivatives can be called secondary securities whose value is Read More
Types of Acquisitions
Hey there! Welcome back once again. Have you ever wondered why do many acquisitions succeed just as many who fail? Read More
Types of Mergers
Hey there! Welcome back again. In the previous blog, we discussed what are mergers and acquisitions. In this blog, we Read More
What are Mergers and Acquisition?
Hey there! Welcome back again. Mergers and Acquisition sound quite familiar right? But ever wondered why are Mergers and Acquisitions Read More
Do Indian Companies Hire CFA’s?
Hey there! So good to have you back again. Are you planning to do CFA and wondering whether Indian companies Read More
What Should I Study, US CMA or Digital Marketing?
Hey there! Welcome back again. Are you confused and wondering which course to study, US CMA or Digital Marketing? Well, Read More
Types or Methods of Business Valuation
Hey there, Welcome back again. Let us understand what business valuation is and its different methods. Let us get started. Read More
What is GST? What Are The Career Opportunities in GST (Tax domain)?
The tax system in India has undergone tremendous changes since the introduction of GST. GST stands for Goods and Services Read More
How to Manage Risks in a Business?
Hey there! Welcome back again. Do you know one of the most critical factors to be kept in mind while Read More
How to Work On a Digital Marketing Project for Practice?
Hey there! Welcome back to another blog. We will be discussing the tips on how to work on a digital Read More
What is Digital Marketing? What is the objective?
Hey there! Ever wondered what is the main objective behind practicing digital marketing techniques? Digital marketing has now become a Read More
Is CA the only optimal career option for commerce graduates?
Are you also thinking about what is next after B.Com? Is pursuing CA the only option for commerce graduates? Let Read More
All about the US CPA course
Topic: Is CPA preferable after CA? Are you a qualified Chartered Accountant and wondering what is next after CA? If Read More
In your opinion, what makes a good Financial Model?
Are you aware that a good financial model can help multiple start-ups and small businesses? With this, now let us Read More
What is Business Valuation?
Business valuation is the general process or result of determining the economic value of a company or a whole business or Read More
Does CFA has any scope in India?
Is it worth becoming a CFA (Chartered Financial Analyst)? Is it worth investing nearly three years, spending about 900 study hours, and Read More
Career Advice: Is doing the ACCA over a CA a better option?
Hey there! So good to have you back again. This blog is mainly for those who are confused regarding which Read More
Which is a Better Career Option, CFA or FRM?
Hey there! Welcome to another blog where we discuss which course is better, the CFA course or the FRM course? We will be Read More
What is the procedure for enrolment for the CPA program for beginners?
Hey there! So good to have you back again. Well, if you are planning to pursue the CPA course then Read More
How Do People Judge the Quality of Financial Modeling?
Hey there! Welcome back again. Are you also wondering what is Financial Modeling, that everyone in the finance industry keeps talking Read More
What is the Reality of a Career in Digital Marketing?
Hey there! Welcome back again. Do you wish to get better clarity on what is the actual reality of a Read More
Which is Better CMA or CIMA?
CMA and CIMA sound quite similar right? Are they the same? Are you also confused and wondering which one is Read More
Is CFA in India Good for a Career?
Hey there! Welcome back again. Are you thinking about how good is the CFA as a career option in India? Let’s deep Read More
I Desire to Get an ACCA Degree, but the Tuition is too Expensive. Why is the ACCA Course Expensive?
Hey there! So good to have you back again. Today, we will be answering the most frequent question which is, Read More
Are There Any Job-Oriented Courses After Completing Graduation?
Hey there! Congratulations on completing your graduation. Are you now ready and excited to pursue job-oriented courses that will help you secure Read More
Is Financial Modeling from EduPristine Worth It?
Hey there! Welcome back again. Let me begin by asking you a very simple question which is, did you know Read More
Does Digital Marketing Have a Great Future Ahead?
Why Digital Marketing course is trending and has so much demand? What topics are covered under the Digital Marketing course syllabus? Is Digital Marketing Read More
What are the Benefits of Pursuing FRM Course(GARP)?
You must have heard about the term FRM or Financial Risk Manager several times, but ever wondered what exactly is FRM, how Read More
What is the Syllabus for CPA Course? Is it the Same as CA or Different?
Hello there! Welcome back again. Are your curious minds also wondering whether the syllabus for the US CPA course is similar to Read More
What are The Top Skills a Commerce Student Must Have?
Hey there! So good to have you back again. Did you know companies are more inclined towards selecting candidates who Read More
What are the Benefits of Learning Financial Modeling?
Do you ever wonder what does a Financial Modeler do? Some of you might also want to become a successful Read More
What is the difference between ACCA and CPA?
Accounting is a field that has endless job opportunities. It is the backbone of an organization. Be it any industry, Read More
5 Reasons why you should pursue the CPA course after CA
CPA course, also known as Certified Public Accountant (CPA), is a globally recognized designation and is the highest standard of Read More
How Opting for Full-Time Level I CFA Course Gives You an Edge Over Others
Chartered Financial Analyst (CFA course) is one of the most in-demand certifications in the field of finance and provides lucrative Read More
A Complete Guide on ACCA Course Eligibility, Duration, Registration, Fees, Etc.
Why the ACCA course? ACCA is a global professional accounting body offering the Chartered Certified Accountant qualification (ACCA) and is Read More
CPA Exam Registrations and Scheduling in India
CPA Exam Registration CPA stands for Certified Public Accountant and is one of the major certification courses in the field Read More
What is Soft Skill Training ?
What is Soft Skill Training With the evolution of the business and client servicing industry, soft skills have started gaining Read More
What is Finance: Types of Finance and Financial Instruments?
Finance is a major and vast topic to cover. Accounting and Finance are often used together, and some even deem Read More
All you want to know about Chartered Accountant (CA)
Here's what you need to get started with the Chartered Accountant (CA) course Chartered Accountant is an honorable designation that Read More
Soft Skills For The Hard World
Soft Skills Training - Reality Check: Whether we'™re talking in a team meeting or presenting in front of an audience, Read More
What is the Importance Of Relative Valuation
Relative Valuation Generally speaking, ‘valuation’ can be defined as the process for finding the ‘value’ of anything. In the world Read More
Ratio Analysis – Ratios Formulae
Ratio analysis'”the foundation of fundamental analysis'”helps to gain a deeper insight into the financial health and the current and probable Read More
Excel Tricks: Text Functions in Excel
How to use Text Functions in Excel Excel is mostly about the numerical data, but at times you can Read More
Explore the Top 12 Opportunities Which Will Take Your Career to the Next Levet [2020 – 2021]]
While writing the last paper of your final B.Com exam, a plethora of thoughts go through your mind. A lot Read More
Top 10 Accounting Firms
Over the years, the way of doing business has changed significantly. There are a number of factors which have contributed Read More
Everything you want to know about the CMA certification
CMA Full Form: Certified Management Accountant (CMA) Going for the CMA certification is a great career move, especially when you Read More
SAP certification – examination, eligibility and benefits
SAP certification help validate the expertise and experience of SAP partners, software users, customers and professionals who are looking to Read More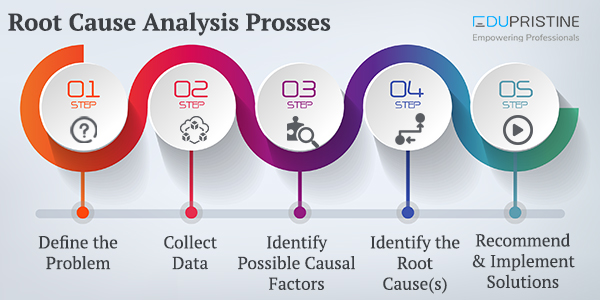
Root Cause Analysis
As the name suggests, Root Cause Analysis deals with identifying the origin of a problem and finding a solution for Read More
Principles and Fundamental Concepts of Basic accounting
Accounting is extremely popular as the language of business language. Through this language, it is easy to analyze the financial Read More
Know how to understand and interpret cash flow statement
A cash flow statement is essential to any business as it can be the basis of budgeting by assessing the Read More
ALL YOU WANT TO KNOW ABOUT SENSITIVITY ANALYSIS
The Crucial Role of Sensitivity Analysis: Hey there, so good to have you back again. Have you ever wondered how Read More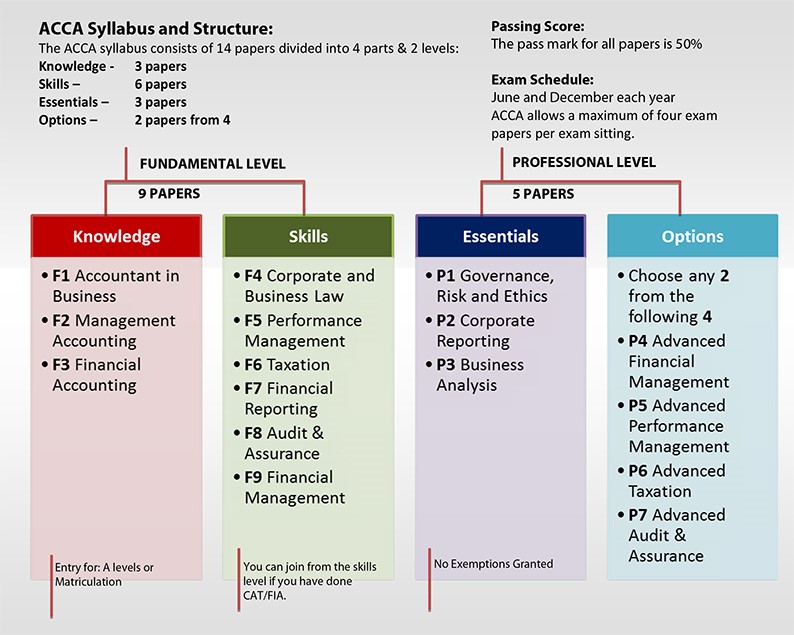
ACCA Full Form
ACCA - Association of Chartered Certified Accountants The role of strategic academic guidance in the life of a student is Read More
FINDING AND REMOVING DUPLICATES IN EXCEL
FINDING AND REMOVING DUPLICATES IN EXCEL Have you ever encountered a situation where you see a lot of duplicated data Read More
Capital Budgeting: Techniques & Importance
In our last article, we talked about the Basics of Capital Budgeting, which covered the meaning, features and Capital Budgeting Read More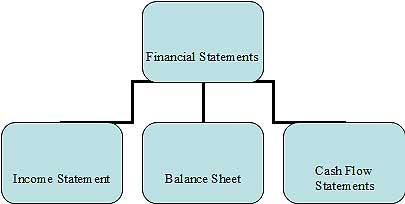
Importance of Business Accounting for enterprises
Introduction: Importance of Accounting to your business The term Accounting is a very common one and we hear about the Read More
Amalgamation Explained in detail
AMALGAMATION EXPLAINED IN DETAIL Understanding Amalgamation: Exploring the Dynamics of Corporate Unions Have you ever wondered what truly defines the Read More
Working Capital Management
What is Working Capital Management? Traditionally, investors, creditors and bankers have considered working capital as a critical element to watch, Read More
STATISTICAL FUNCTIONS IN EXCEL
STATISTICAL FUNCTIONS IN EXCEL People usually have love-hate relationship with statistics. When you get your formulas right you are in Read More
Venture Capital
Unlocking the power of Venture Capital: Features, Financing Methods, and Opportunities Hey there, so good to have you back again! Read More
Financial Reporting
In any industry, whether manufacturing or service, we have multiple departments, which function day in day out to achieve organizational Read More
Cell References in Excel
While using excel, there may be times when you want to keep the values same while copying formulas. This can Read More
Costing Methods & Important Cost Terms
Costs can be simply defined as the money or resources associated with a purchase / business transaction or any other Read More
Balance sheet explained in detail
What is Balance Sheet? A balance sheet (also called the statement of financial position), can be defined as a statement Read More
Cash Flow Statement
CASH IS KING;is a known fact, that it is the basis of any business. No bills, employees or for that Read More
What are the career options after Mcom
Master of Commerce or M Com is a postgraduate Master Degree which specializes in commerce, accounting, management and economics related Read More
WHAT IS STANDARD DEVIATION?
WHAT IS STANDARD DEVIATION? In finance and investment, understanding and managing risk is of paramount importance. Among the tools available Read More
Know how effective is CMA course compared to MBA in providing a dream job
There are various industries and sectors out there where you can grow and enhance your career. Management, Accounting, Finance, Engineering, Read More
ACCA EXAM STRUCTURE AND PATTERN
ACCA EXAM STRUCTURE AND PATTERN Understanding the ACCA exam structure and pattern is essential for individuals aspiring to pursue a Read More
Comparison of CPA course with other courses
The Accounting industry offers you various opportunities to learn via various courses. You can choose which one suits your academic Read More
Advantages and Application Process of FRM
FRM (Financial Risk Manager) Certification gives you a distinctive edge from the other risk management professionals operating in the Finance Read More
An insight into OTC Derivatives
What is Derivatives? Derivatives are defined as the type of security in which the price of the security depends/is derived Read More
CPA Course Syllabus – Topics and Importance
A CPA requires a broad spectrum of knowledge and proficiency in it. The purpose of CPA exam syllabus is to Read More
CFA® Study Planner
Most of the CFA® pursuers believe that CFA® Program tests are very difficult and arduous but that is not the Read More
CPA Course details, application fees and benefits of doing it
A Certified Public Accountant (CPA) is the highest standard of competence in the field of Accountancy across the globe. The Read More
All Important About CFA® LEVEL 1 Syllabus
CFA® charter is one of the most exalted credentials of those who work in the financial sector or who make Read More
All about Portfolio Management
What is a Portfolio? A portfolio can be defined as different investments tools namely stocks, shares, mutual funds, bonds, cash Read More
Cost Management: Meaning, Techniques & Advantages
What is Cost? Cost is defined as the monetary valuation of effort, material, resources, time consumed, risk and opportunity forgone Read More
How to get into Big 4 Accounting Firms?
We all have some career objectives and aspirations. For higher studies like MBA, CA, CPA, ACCA, CFA etc. one has Read More
FRM Question Bank
For every exam, time management is very important and everyone wants a precise course content in a prioritized manner along Read More
Top 10 Companies that hire CFA® Charterholders
A lot of hardwork and investment is required to prefix the words CFA® Program before your name and time and Read More
Income Statement in detail
WHAT IS INCOME STATEMENT? The income statement is one of the important primary financial statements provided by organizations. It presents Read More
KPIs for Business Analysts
A business analyst's role in an IT project is to ensure that all requirements of the client are captured and Read More
Annual Report
What is an Annual Report: The single source of getting information about any company whether it is the past or Read More
Capital Budgeting
WHAT IS CAPITAL BUDGETING? Capital budgeting is a company’s formal process used for evaluating potential expenditures or investments that are Read More
Mergers and Acquisitions
What is Mergers & Acquisitions? Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are defined as consolidation of companies. Differentiating the two terms, Mergers Read More
Detecting Multicollinearity
" In my previous blog “ How to deal with Multicollinearity ”, I theoretically discussed about definition of multicollinearity and Read More
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT OF A COMPANY
ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT OF A COMPANY One of the major aspects of making a sound investment decision is analyzing Read More
8 Excel functions that every Data Analyst must know
Are you a data analyst or looking for a career as a data analyst??? Well then, today's article is dedicated Read More
Duckworth-Lewis Method
Duckworth-Lewis method(D/L method) is a mathematical function defined to set and calculate the target score for the team batting second Read More
6 Most Common Excel Errors
Hashtags look cool when seen on Twitter or Facebook but as soon as they start appearing in Excel sheet, you Read More
RULE PRECEDENCE IN CONDITIONAL FORMATTING
RULE PRECEDENCE IN CONDITIONAL FORMATTING Conditional Formatting in Excel makes tasks easier and more user-friendly but it can sometimes be Read More
Types of Investment Banking jobs
Investment banking is one of the most attractive industry to work in. not only for people with formal education in Read More
FRM Part 1 syllabus
Shut your doors, drop the drapes on your windows and don't bother looking at the clock because it's always the Read More
Ratio Analysis – Introduction
Introduction The term 'ratio analysis'refers to the analysis of the financial statements in conjunction with the interpretations of financial results Read More
Ratio Analysis – Classification of ratios and Liquidity Ratio
In our previous blog post we discussed ratio analysis. In this blog post we will explain classification of ratios and Read More
Bootstrapping Solution
What is the Bootstrapping method? Bootstrapping is a method for constructing a zero-coupon yield curve from the prices of a Read More
Dell’s Leveraged Buyout: A Real-life Case Study
Acquisitions Acquisitions or takeovers are a transaction or process wherein one company (commonly called as acquirer) or an investor acquires Read More
CASH FLOW STATEMENT: LEARN TO CREATE CASH FLOW STATEMENT TEMPLATE IN EXCEL
CASH FLOW STATEMENT: LEARN TO CREATE CASH FLOW STATEMENT TEMPLATE IN EXCEL Welcome to our following how-to guide: How to Read More


Leave a Reply